Calibration process is described by
- Calibration quality stipulating approximation method to correlate data,
- Lateral discretization to account for scanner sensor to sensor variations,
- Dose prefiltering to mitigate noise and noise related artifacts.
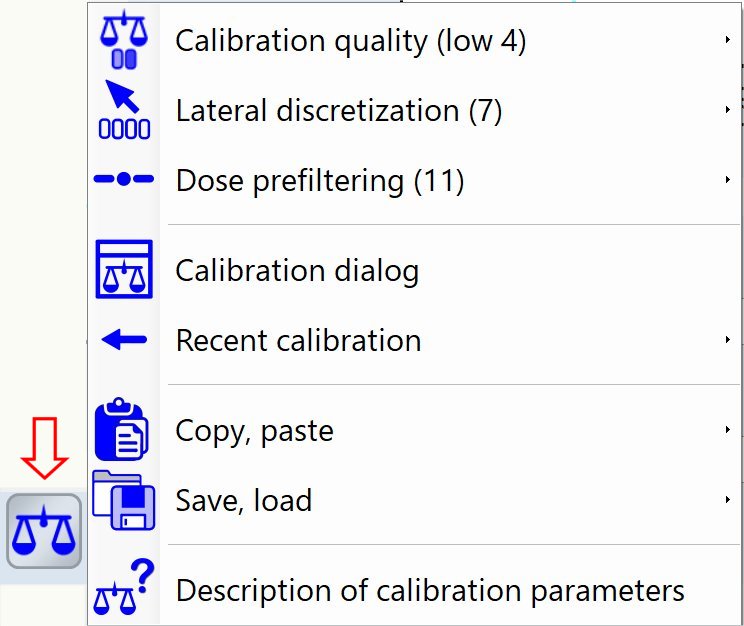
All calibration parameters can be accessed through the context menu via the 'Libra' button at bottom center
Calibration Quality
Calibration quality stipulates the approximation method of the correlation and is described by
-
Approximation order
Polynomial order used to approximate calibration data.
- Low order highly stable (always produces result), but more modest accuracy.
- High order high accuracy for smooth data, but may be instable when data distorted (may not deliver a result).
-
Dose sections
Total dose range is splitted into sections (equi-sized subintervals)
and each section is calibrated separately.
The calibrations for the dose section are smoothly attached
to each other to have a smooth approximation over the entire dose
range avoiding any ‘jump’ in dose values.
- Smaller dose range means usually better approximation, i.e better accuracy is achieved. This approach works well when calibration data are sufficient smooth.
- Low order for each section makes resulting method more stable and small enough dose sections (i.e. if number of sections high enough) produce better calibration accuracy. This approach works well when calibration data are sufficiently equi-distributed (e.g. calibration step wedge many dose levels).
Calibration quality context menu
Context menu shown below has 3 selection groups:
- Single dose section approximation,
- Multiple dose section.
- Legacy
 |
Minimum requirments |
Linear data approximation over entire dose calibration range.
Most stable approximation method Minimum required data: Single strip exposure and unexposed 0 Gy strip. |
 |
Low approximation order |
Quadratic polynomial approximation over full calibration range.
Data requirements: Wedge with 3 or more dose levels. |
 |
Medium order |
Cubic polynomial approximation over full calibration range.
Data requirements: Wedge with 4 or more dose levels. |
 |
High order |
Quartic polynomial approximation over full calibration range.
Data requirements: Wedge with 5 or more dose levels. |
 |
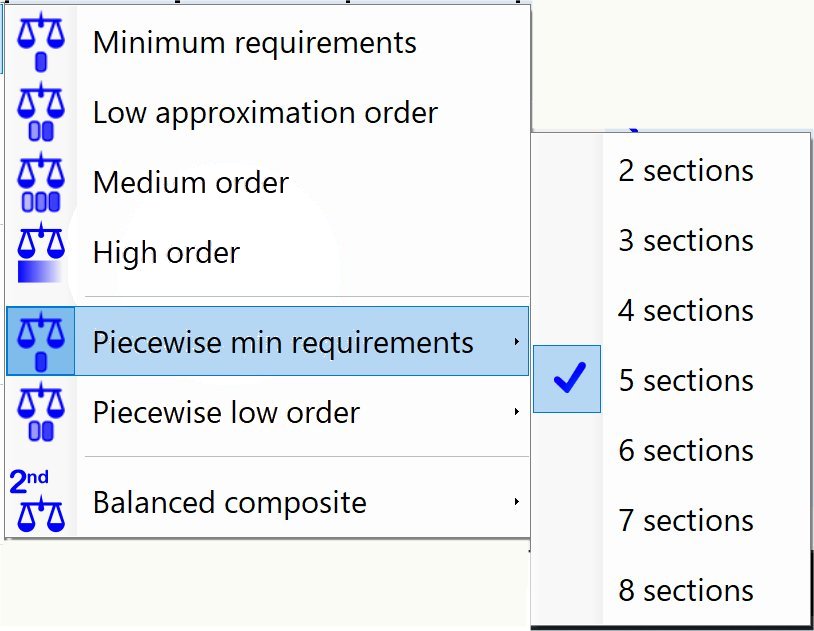
Piecewise min requirments |
Linear polynomial approximation over multiple calibration dose sections.
Very stable approximation with high accuracy at higher number of dose sections. Data requirements: Wedge with 3 or more dose levels. |
 |
Piecewise low order |
Linear polynomial approximation over multiple calibration dose sections.
Highly accurate method, very stable approximation with lower number of dose sections. Default method for calibration quality. Data requirements: Wedge with 3 or more dose levels. |
 |
Balanced composite | Legacy calibration protocol (balanced composite) using secondary scan with calibration data. |
Lateral Discretization
Lateral discretization stipulates the calibration resolution,
i.e. how many horizontal image pixels (scanner sensors) are used per calibration.
Lateral Discretization context menu
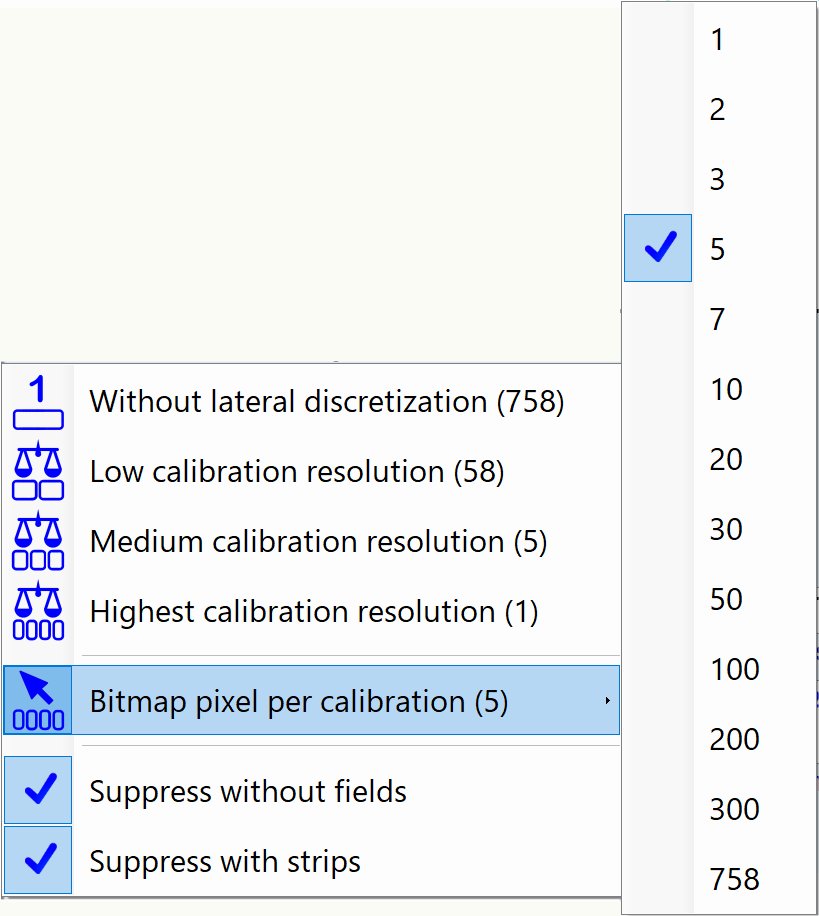
Each item in the context menu includes the number of image pixels per calibration that will be selected.
 |
Without lateral discretization |
Single calibration correlation is used for all scanner sensors (all lateral locations).
Highest number of image pixels per calibration. No compensation of lateral scanner variations, maximum averaging of film non-uniformity variations. |
 |
Low calibration resolution |
Recommended low number of calibrations.
High number of image pixels per calibration. Adaptive to used calibration quality and width of the scanned image. |
 |
Medium calibration resolution |
Recommended medium number of calibrations.
Medium number of image pixels per calibration. Adaptive to used calibration quality and wdith of the scanned image. |
 |
Highest calibration resolution |
Recommended highest number of calibrations.
High number of image pixels per calibration. Adaptive to used calibration quality and width of the scanned image. |
 |
Bitmap pixel per calibration |
Select the number of pixels per calibration.
1 pixel per calibration - each sensor is calibrated separately, best compensation of lateral scanner variation, Note:The less pixels per calibration are used |
| Suppress without fields | If selected and a calibration field is not available the lateral discretization is suppressed. | |
| Suppress with strips | If selected, the lateral discretization is suppress when calibration strip is present. |
Dose Prefiltering
Dose prefiltering context menu
Filter selected in the context menu shown below is applied directly to the film scan before dose conversion.
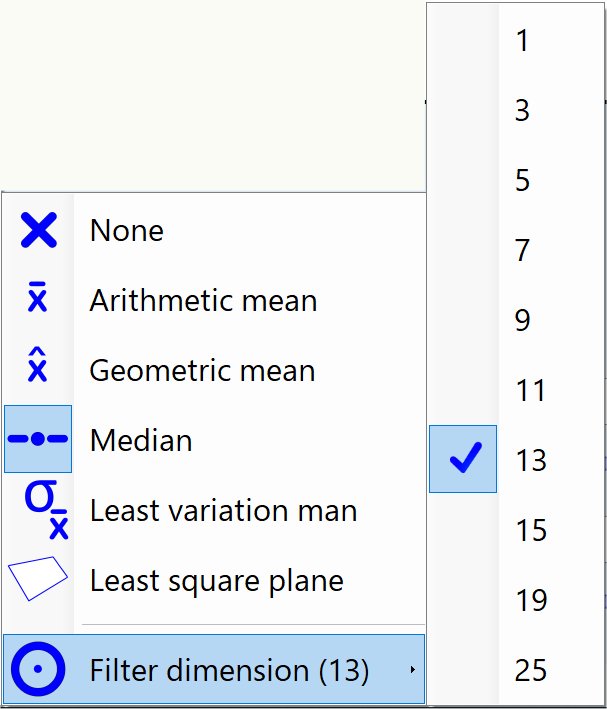
 |
None | No filtering is applied. |
 |
Arithmetic mean | Arithmetic average across the sampled points is applied. |
 |
Geometric mean | Geometric average across the sampled points is applied. |
 |
Median | Median value across the sampled points is applied. |
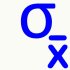 |
Least variation mean | Non-linear Kuwahara filter is applied to smooth the data. |
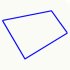 |
Least squares plane | Least squares plane is fitted to the sample data and plane value at filter position is used. |
 |
Filter dimension | Filter dimension is the diameter of the circular region centered at filter location. |




